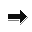
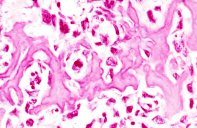
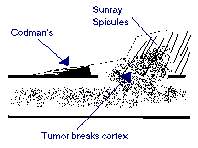
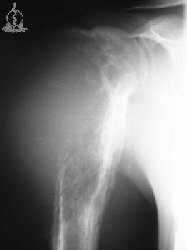
OsteosarcomaOsteosarcoma is a primary malignancy of bone. The malignant cells produce osteoid.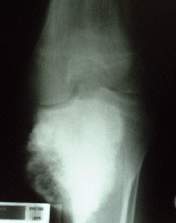 Histologically the tumor
is composed of malignant osteoblasts which produce osteoid Most occur in
the metaphysis of long bones especially about he knee. Age - 10 to 20 years.
If seen later in life consider a secondary malignancy ( to Paget's
or post irradiation) It metastases to the lungs and to other bones. Histologically the tumor
is composed of malignant osteoblasts which produce osteoid Most occur in
the metaphysis of long bones especially about he knee. Age - 10 to 20 years.
If seen later in life consider a secondary malignancy ( to Paget's
or post irradiation) It metastases to the lungs and to other bones.
PrognosisPoor in South Africa (20% 5 yr. survival, because of late presentation). International experience is towards a 60% survival.
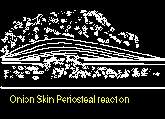
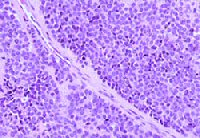
Ewing's SarcomaEwing's is a small cell tumor seen in the 10 to 25 yr. age group. 60% occur in the long bones, but the scapula and pelvis are often affected.
Ewing's is one of the few tumors that frequently originate in the shaft
of long bones. 50% originate in the diaphysis. It is an osteolytic tumor
and has a large soft tissue component. It may mimic chronic osteomyelitis
and even produce a raised body temperature and ESR as well as white cell
count. Histologically the tumor consists of monotonous sheets of small
round cells.
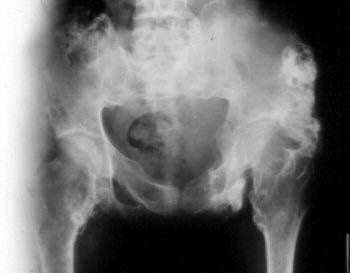
MyelomaMyeloma is a common primary tumour from the 5th decade onwards. Myeloma presents with lytic bone lesions which commonly lead to pathological fracture.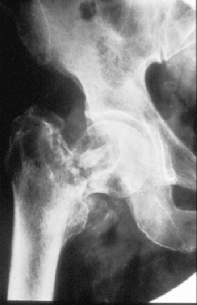 Site Common in any bone containing red marrow especially flat bones eg pelvis as well as vertebra. Consider the diagnosis in a vertebral fracture in the elderly. Typically the vertebra is flattened the so called "wafer" vertebra. If there is systemic involvement the skull x-ray may show "punched out" lytic lesions. Clinically Affects bone containing red marrow (skull, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, pelvis) Weakness, bone pain and pathological fractures Backache is common and may cause root pain and occasionally paraplegia Anemia, generalised malaise and cachexia
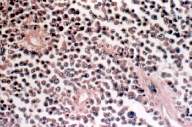
HistologyThe tumor is composed of abnormal plasma cells. If the tumor is localised to one bone it is known as a plasmacytoma Systemic involvement is known as multiple myeloma A bone marrow biopsy must be done from the pelvic rim to determine the extent of spread.
|
ChondrosarcomaChondrosarcoma usually presents after 6th decade. Characteristically chondrosarcoma is slow growing and seen proximally in the skeleton e.g. prox. humerus and pelvis.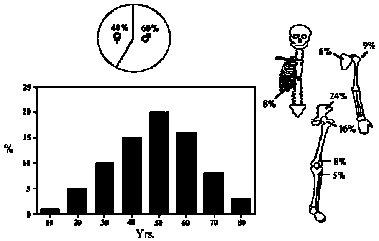
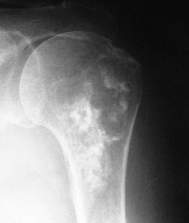
Secondary Chondrosarcoma TreatmentSurgery alone is the only hope of cure with this tumour. Chondrosarcoma
is unresponsive to irradiation and chemotherapy. Block excision is recommended.
|